Paediatric fractures.
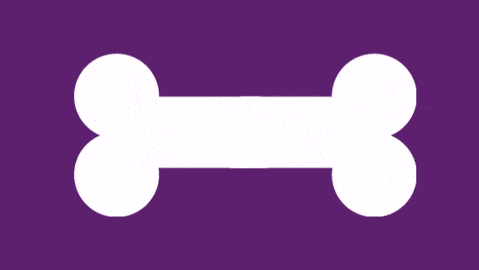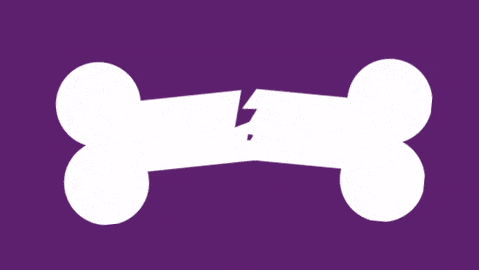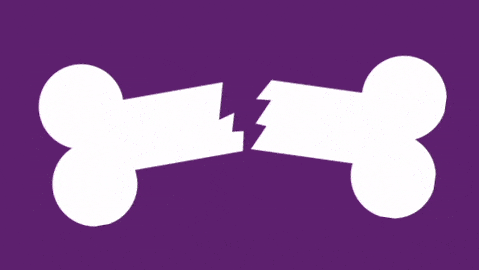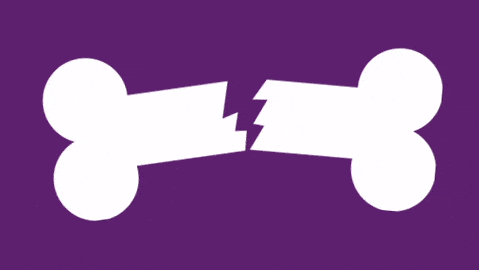
What grade of Salter Harris fracture is this injury?
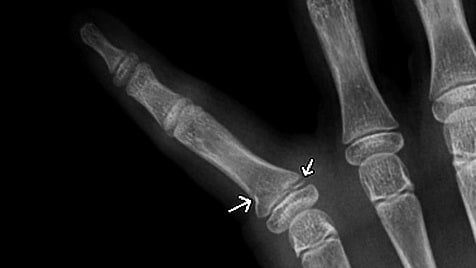
The fracture is above the growth plate. Below is a link to Rebel EM showing the classification of 1 to 5.
What nerve injury would you suspect in this 9yr old girl?
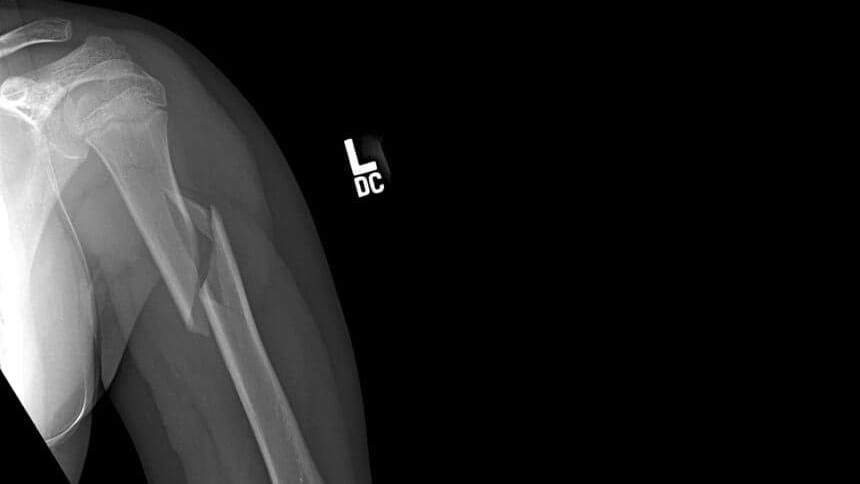
You should suspect injury to the radial nerve as it sits in the spiral groove of the humerus.
Test for the radial nerve by finger and wrist extension as well as sensation over the dorsum of the thumb.
Which of the following is a recognised way to reduce a "pulled elbow"?
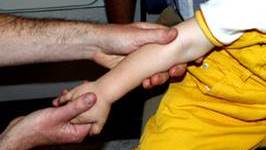
Remember analgesia. Also if there is swelling or bruising or the mechanism is not consistent with a pulled elbow please xray first. That way you will not be pulling on a supracondylar fracture.
This xray was taken folllowing a fall in a 6yr old. It shows "bowing" of the radius and ulnar. Which of the following is TRUE about this injury?
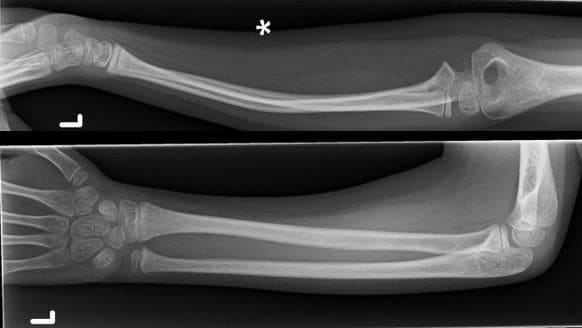
An unusual injury. Occurs almost exclusively in children with a longitudinal stress.
Make sure there are no associated fractures and consult orthopaedics.
Microscopic examination shows microfractures that you cannot see on an xray.
What is the most common fracture in paediatrics?

Probably predictable as you place your extended arm down when you fall.
What is this injury called?
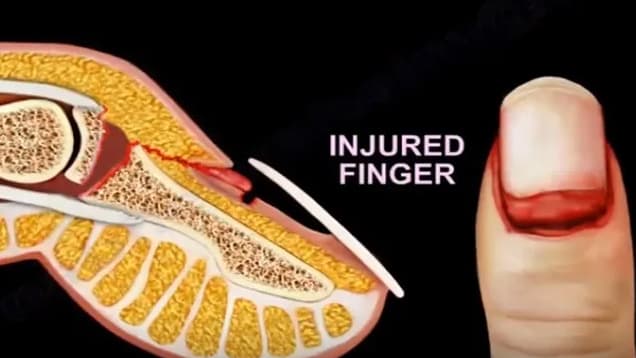
Seymour fracture is a displaced distal pharyngeal physeal fractures with an associated nailbed injury.
Treatment is usually Antibiotics, open reduction in theatre with pinning and repair of the nailbed.
Which of the following injuries would "buddy strapping" NOT be appropriate?
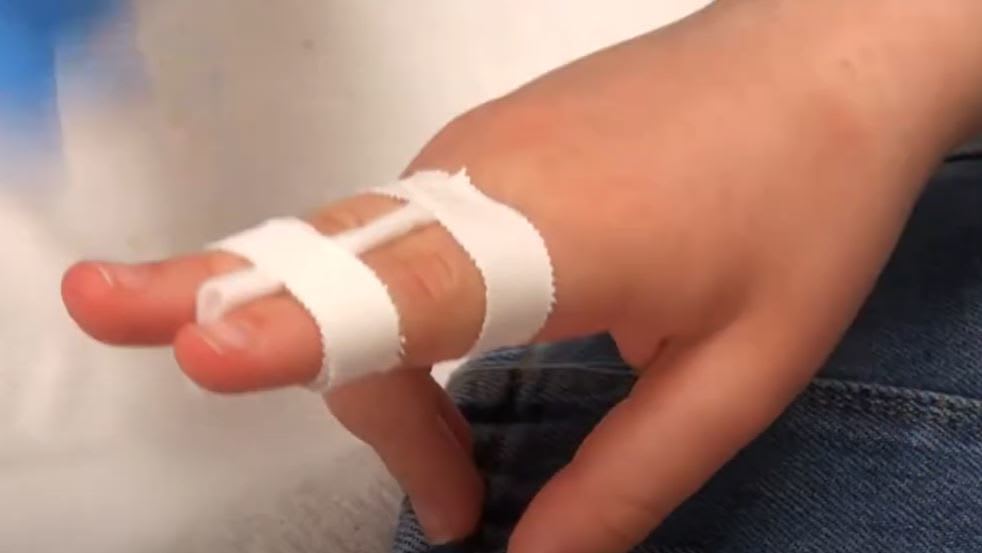
It is a very useful technique.
Below is a good simple video showing it being put on.
If there is rotation then the fracture needs orthopaedic input and probably a K wire.
Which of the following fractures is NOT considered a "Red flag" for Non Accidental Injury?

Always consider the possibility of NAI in an injured child.
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a congenital bone disease. Which of the following is TRUE?

It is a very heterogenous group. They have blue sclera. It is equally distributed between girls and boys and is due to abnormal Type 1 Collagen production.
If you are interested read Quentin Kenihan's memoir "Not all superheroes wear capes".
Musa Dayib, a 14mth old boy, survived a fall from a balcony in 2014. How many floors up was the balcony?

It was about 35 metres. He suffered concussion, some fractured ribs, and a pneumothorax.
Incidentally the highest fall survived without a parachute was Vesna Vulovic who was a flight attendent and fell 33,338 ft (10.16km). A briefcase bomb blew up the plane. She almost completely recovered and afterwards had no fear of flying.